PH13-8 Mo UNS S13800/Werkstoff 1.4548 stainless steel
overview
PH 13-8 Mo stainless is a martensitic precipitation/age-hardening stainless steel capable of high strength and hardness along with good levels of resistance to both general corrosion and stress-corrosion cracking. the alloy exhibits good ductility and toughness in large sections in both the longitudinal and transverse directions. Compared to other ferrous-based materials, this alloy offers a high level of useful mechanical properties under severe environmental conditions.
13-8 Mo stainless has good fabrication characteristics and can be age-hardened by a single low temperature treatment.
13-8 Mo stainless has been used for valve parts, fittings, cold-headed and machined fasteners, shafts, landing gear parts, pins, lockwashers, aircraft components, nuclear reactor components and petrochemical applications requiring resistance to stress-corrosion cracking.
Limiting Chemical Composition, %
iron..............................................................................................................................................................................................balance
Chromium...........................................................................................................................................................................12.25--13.25
Nickel.......................................................................................................................................................................................7.50--8.50
Molybdenum............................................................................................................................................................................2.00--2.50
Aluminium...............................................................................................................................................................................0.90--1.35
Manganese...............................................................................................................................................................................1.00 max.
Nitrogen....................................................................................................................................................................................0.01 max.
Silicon........................................................................................................................................................................................1.00 max.
Carbon........................................................................................................................................................................................0.05 max.
Phosphorus................................................................................................................................................................................0.01 max.
Sulphur......................................................................................................................................................................................0.008 max.
Physical Constants
Below are some physical constants and thermal properties of
Density |
g/cm³.................................................................................................7.76 |
Melting Point: |
°C......................................................................................................1404 |
Thermal conductivity at 20°C |
W/m · °C............................................................................................12.8 |
Elongation coefficient at 20-100°C |
μm/m · °C.............................................................................................13 |
Mechanical properties
Properties |
Metric |
Imperial |
Tensile strength |
1516 MPa |
220 ksi |
Yield strength |
1413 MPa |
205 ksi |
Elongation at break |
10% |
10% |
Hardness, Rockwell C |
45 |
45 |
Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel PH13-8 Mo level of general-corrosion reistance is greatest in the fully hardened condition and decreased slightly as the aging temperature is increased. Numerous tests representing a marine environment have shown the alloy, in both the wrought and welded conditions, to have a high level of resistance to stress-corrosion cracking. For best resistance to stress-corrosion cracking, a minimum aging temperature of 1000°F (538°C) is suggested.
For optimum corrosion resistance, surfaces must be free of scale and foreign particles and finished parts should be passivated.
Heat Treatment
PH 13-8 Mo Precipitation Hardening Alloy is produced in the annealed condition. This is also called the solution heat treated condition, or Condition A. Solution treat from 1675 to 1725°F (910 to 940°C) for 15 to 30 minutes at temperature. Air cool or oil quench to below 60°F (15°C) to effect complete transformation to martensite. Aging is normally carried out from 950 to 1150°F (510 to 620°C), depending upon the desired final properties. Heat treatment is usually performed in air. Heat treatment of brazed components may be done in inert atmospheres. Reducing atmospheres should not be used because of the potential for hydrogen contamination.
WELDING
Weldability Carpenter 13-8 stainless can be welded using the inert-gas shielded or resistance welding processes. When a filler metal is required, 13-8 welding consumables should provide welds with properties similar to those of the base metal. When designing the weld joint, care should be exercised to avoid stress concentrators, such as sharp corners, threads, and partial- penetration welds. When high weld strength is not needed, a standard austenitic stainless filler, such as E/ER308L, should be considered. Normally, welding in the solution-annealed condition has been satisfactory; however, where high welding stresses are anticipated, it may be advantageous to weld in the overaged (H 1150) condition. Usually, preheating is not required to prevent cracking. If welded in the solution-treated condition, the alloy can be directly aged to the desired strength level after welding. However, the optimum combination of strength, ductility and corrosion resistance is obtained by solution treating the welded part before aging. If welded in the overaged condition, the part must be solution treated before aging.
Available Forms
We provide you with a variety of product forms, including but not limited to
● Bar & Rod
● Pipe & Tube
● Coil & Strip
● Plate & Sheet & Circle
● Wire & Welding
● Fitting (Flange, Elbow, Tee...)
● Customize
description2


 Inconel 625
Inconel 625 Inconel 718
Inconel 718 Inconel 725
Inconel 725 Inconel X-750
Inconel X-750 Inconel 690
Inconel 690 Inconel 617
Inconel 617 Inconel 601
Inconel 601 Inconel 600
Inconel 600 Inconel 686
Inconel 686 Inconel 602CA
Inconel 602CA Incoloy A-286
Incoloy A-286 Incoloy 825
Incoloy 825 Incoloy 925
Incoloy 925 Incoloy 926
Incoloy 926 Incoloy 800
Incoloy 800 Incoloy 800H
Incoloy 800H Incoloy 800HT
Incoloy 800HT Incoloy 909
Incoloy 909 Incoloy 31
Incoloy 31 Incoloy 901
Incoloy 901 Monel K-500
Monel K-500 Monel 400
Monel 400 Nimonic 263
Nimonic 263 Nimonic 75
Nimonic 75 Nimonic 80A
Nimonic 80A Nimonic 90
Nimonic 90 Nimonic PE11
Nimonic PE11 Nimonic PE16
Nimonic PE16 Nimonic PK33
Nimonic PK33 Nimonic 901
Nimonic 901 Nimonic 81
Nimonic 81 Nimonic 86
Nimonic 86 Nimonic 105
Nimonic 105 Nimonic 115
Nimonic 115 Hastelloy C-276
Hastelloy C-276 Hastelloy C
Hastelloy C Hastelloy C4
Hastelloy C4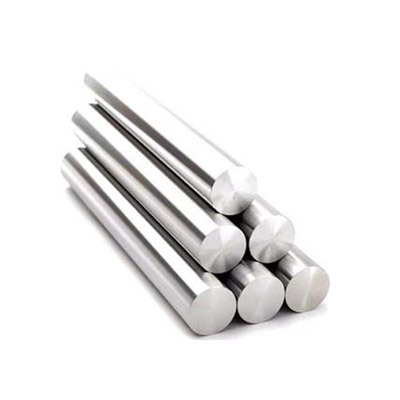 Hastelloy C-22
Hastelloy C-22 Hastelloy C-2000
Hastelloy C-2000 Hastelloy B-2
Hastelloy B-2 Hastelloy B-3
Hastelloy B-3 Hastelloy G30
Hastelloy G30 Hastelloy X
Hastelloy X Super Invar 32-5(4J32)
Super Invar 32-5(4J32) Alloy 36(4J36)
Alloy 36(4J36) Alloy 42(4J42)
Alloy 42(4J42) Alloy 50(1J50)
Alloy 50(1J50) Hiperco 50(1J22)
Hiperco 50(1J22) Alloy 46
Alloy 46 Permalloy (1J79)
Permalloy (1J79) Supermalloy(1J85)
Supermalloy(1J85) ERNiCrMo-2
ERNiCrMo-2 ERNiCrMo-3
ERNiCrMo-3 ERNiCrMo-4
ERNiCrMo-4 ERNiCrFe-7
ERNiCrFe-7 ERNiCrFe-7A
ERNiCrFe-7A ERNiCrMo-10
ERNiCrMo-10 ERNiCrCoMo-1
ERNiCrCoMo-1 ERNiFeCr-2
ERNiFeCr-2 ERNiFeCr-1
ERNiFeCr-1 ERNiMo-8
ERNiMo-8 ERNiCrMo-13
ERNiCrMo-13 ERNiCr-4
ERNiCr-4 ERNiCr-3
ERNiCr-3 ERNi-1
ERNi-1 Haynes-25
Haynes-25 Hayness-188
Hayness-188 MP35N
MP35N Refractory 26
Refractory 26 Waspaloy alloy
Waspaloy alloy 17-4PH
17-4PH 17-7PH
17-7PH 904L
904L Nitronic 50
Nitronic 50 Nitronic 60
Nitronic 60 AL-6XN
AL-6XN F55
F55 PH 13-8
PH 13-8 Haynes-230
Haynes-230 Nickel 200
Nickel 200 Cr20Ni80
Cr20Ni80 Sheet & Plate
Sheet & Plate Strip & Foil
Strip & Foil Bar & Rod
Bar & Rod Pipe & Tube
Pipe & Tube Bolts & Fasteners
Bolts & Fasteners Flange & Ring
Flange & Ring Nickel Alloy Powder
Nickel Alloy Powder